

In the ever-evolving landscape of fuel management, the demand for efficient and reliable Fuel Transfer Pumps is more critical than ever. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global fuel transfer pump market is projected to grow from USD 1.8 billion in 2021 to USD 2.5 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7%. This growth is driven by the increasing necessity for safe fuel transfer solutions across various industries, including automotive, aviation, and construction. As organizations seek alternatives to conventional fuel transfer methods, understanding the mechanics behind Fuel Transfer Pumps becomes essential.
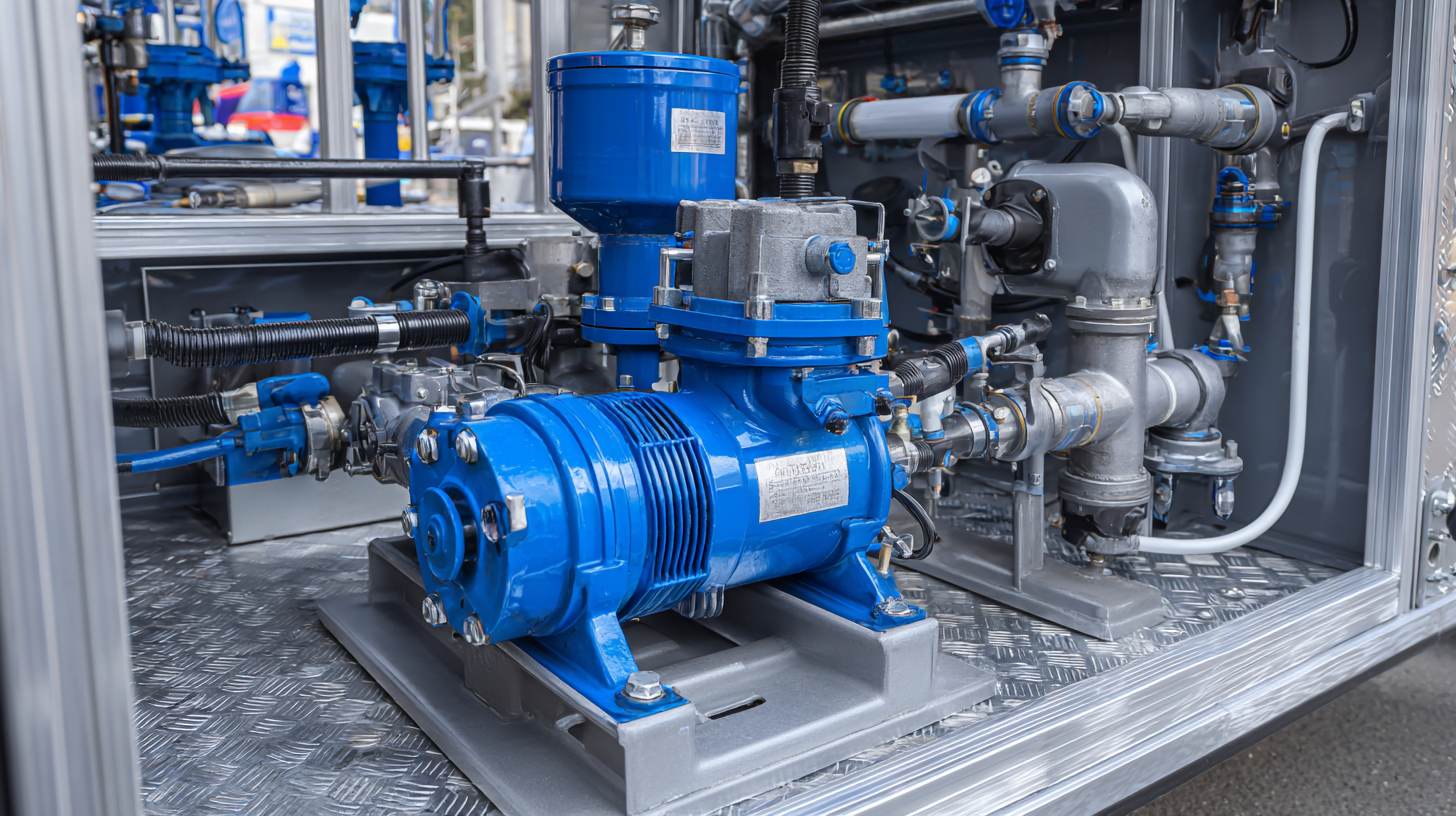

This blog will explore the various types of fuel transfer pumps available in the market, their operational principles, and how they cater to the diverse needs of different sectors. By delving into these alternatives, we can better appreciate the role of Fuel Transfer Pumps in optimizing fuel transfer processes while ensuring efficiency and safety.
Fuel transfer pumps are essential tools in various industries, serving to move fuel from one location to another efficiently and safely. There are several types of fuel transfer pumps, each designed for specific applications and environments. One of the most common types is the electric fuel transfer pump, which relies on electric power to facilitate the pumping process. These pumps are popular in commercial settings due to their ease of use and ability to handle large volumes of fuel quickly.
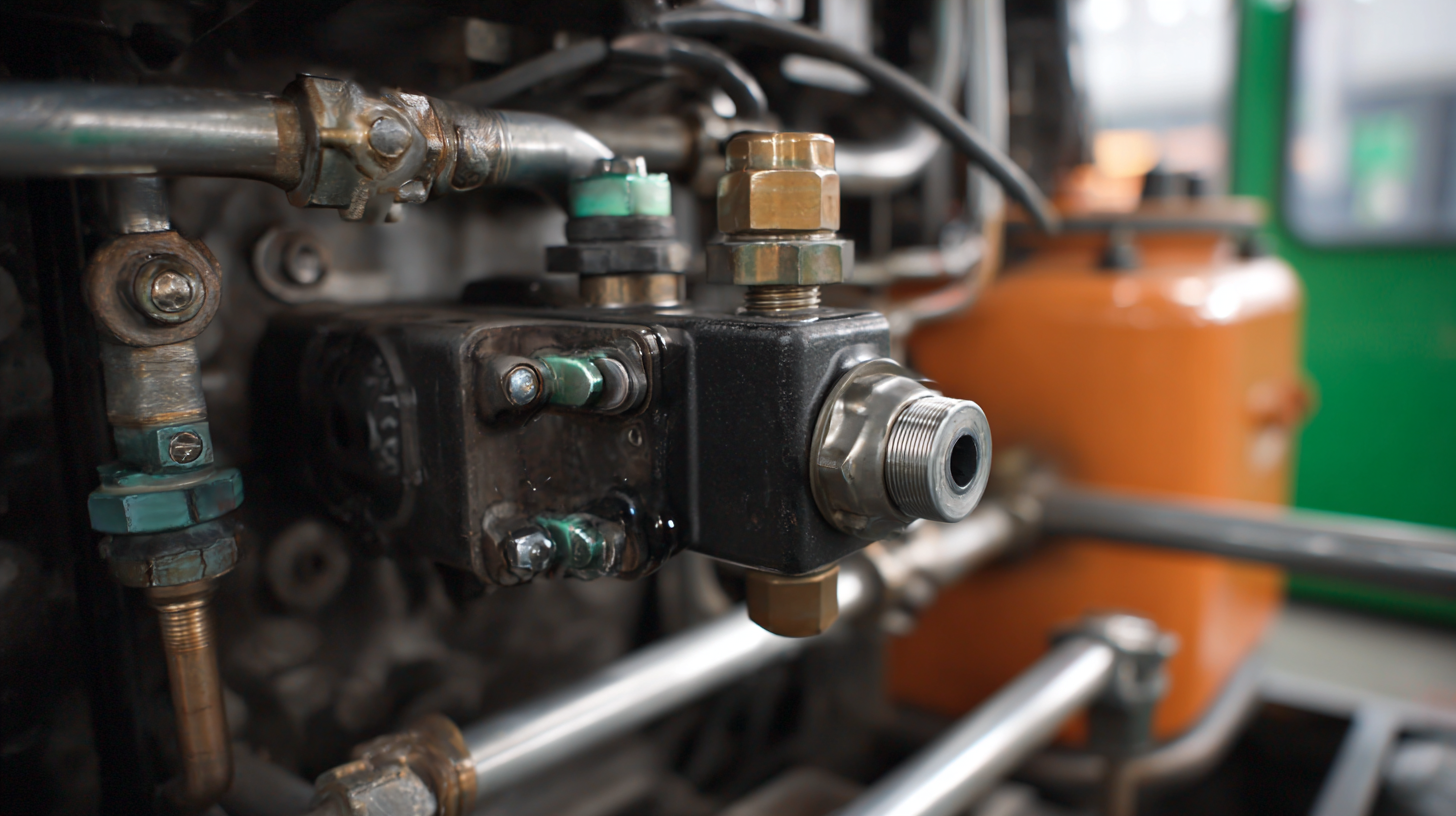
Fuel transfer pumps are essential components in various industries, ensuring the efficient and safe transfer of liquids such as gasoline, diesel, and other fuels. The internal mechanics of these pumps are designed to optimize both the flow rate and the pressure of the fuel being transferred. Most fuel transfer pumps operate using positive displacement or centrifugal mechanisms. Positive displacement pumps move fluid by trapping a fixed amount and forcing it into the discharge pipe, making them ideal for high-viscosity fluids. In contrast, centrifugal pumps utilize rotational energy to create a vacuum that draws fluid in, providing a continuous flow suitable for low-viscosity fuels.
Industry reports indicate that the global market for fuel transfer pumps is expected to grow significantly, reaching nearly $3 billion by 2025, driven by the rising demand in sectors like automotive, aviation, and agriculture. This growth hinges on technological advancements in pump design, such as improved efficiency and reduced emissions. For instance, the implementation of advanced materials and coatings in pump construction can enhance durability and performance, minimizing maintenance costs while maximizing operational uptime. Understanding these internal mechanics enables operators to choose the appropriate pump for their specific application, leading to enhanced fuel management and safety.
| Feature | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Pump Type | Positive Displacement, Centrifugal | Moves fuel through a system efficiently |
| Power Source | Electric, Mechanical, Manual | Provides the necessary energy for operation |
| Flow Rate | Varies by model, typically 5-100 GPM | Determines how quickly fuel is transferred |
| Materials | Aluminum, Stainless Steel, Plastics | Influences durability and resistance to corrosion |
| Applications | Fuel stations, shipping, agriculture | Used for transferring fuel in various industries |
| Safety Features | Leak prevention, automatic shut-off, grounding | Ensures safe operation during fuel transfer |
Fuel transfer pumps play a crucial role across various industries, facilitating the reliable and efficient movement of fuel in diverse applications. As the mobile fuel pumps market anticipates significant growth, projected to reach USD 6.1 billion by 2033, the demand for these essential tools continues to rise. Industries such as oil and gas, transportation, and construction rely on fuel transfer pumps not only for their mobility but also for their ability to streamline operations and reduce downtime.
In applications ranging from refueling vehicles to transferring fuel at remote job sites, understanding the specific needs of each sector is paramount. For instance, the automotive industry has a burgeoning market for fuel feed pumps, projected to grow significantly over the next decade. With advancements in technology, designs are becoming more efficient, leading to increased performance and lower environmental impact.
**Tips:** When selecting a fuel transfer pump, consider not only the motor type and power source but also the mounting options that best suit your operational needs. Additionally, regular maintenance and monitoring can significantly extend the life of your pump, ensuring seamless operation in critical situations. Always assess the specific requirements of your industry and applications to make informed choices that enhance productivity and efficiency.
When choosing a fuel transfer pump, several critical factors come into play to ensure optimal performance and safety. One of the foremost considerations is the pump's flow rate. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, an efficient fuel transfer pump should have a flow rate compatible with the specific application—typically ranging from 5 to 80 gallons per minute (GPM) for most commercial operations. A pump that meets these requirements not only minimizes transfer time but also reduces the risk of fuel contamination due to prolonged exposure.
Another key factor is the pump's compatibility with the type of fuel being transferred. Data from the National Association of Manufacturers indicates that different fuels, such as diesel, gasoline, or biofuels, may require specialized materials to prevent corrosion or degradation. For instance, pumps made from aluminum alloys or stainless steel are often preferred for diesel applications, while those transferring gasoline may need specific elastomers to handle volatile compounds. Thus, understanding the technical specifications and material compatibilities is vital for maintaining pump integrity and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
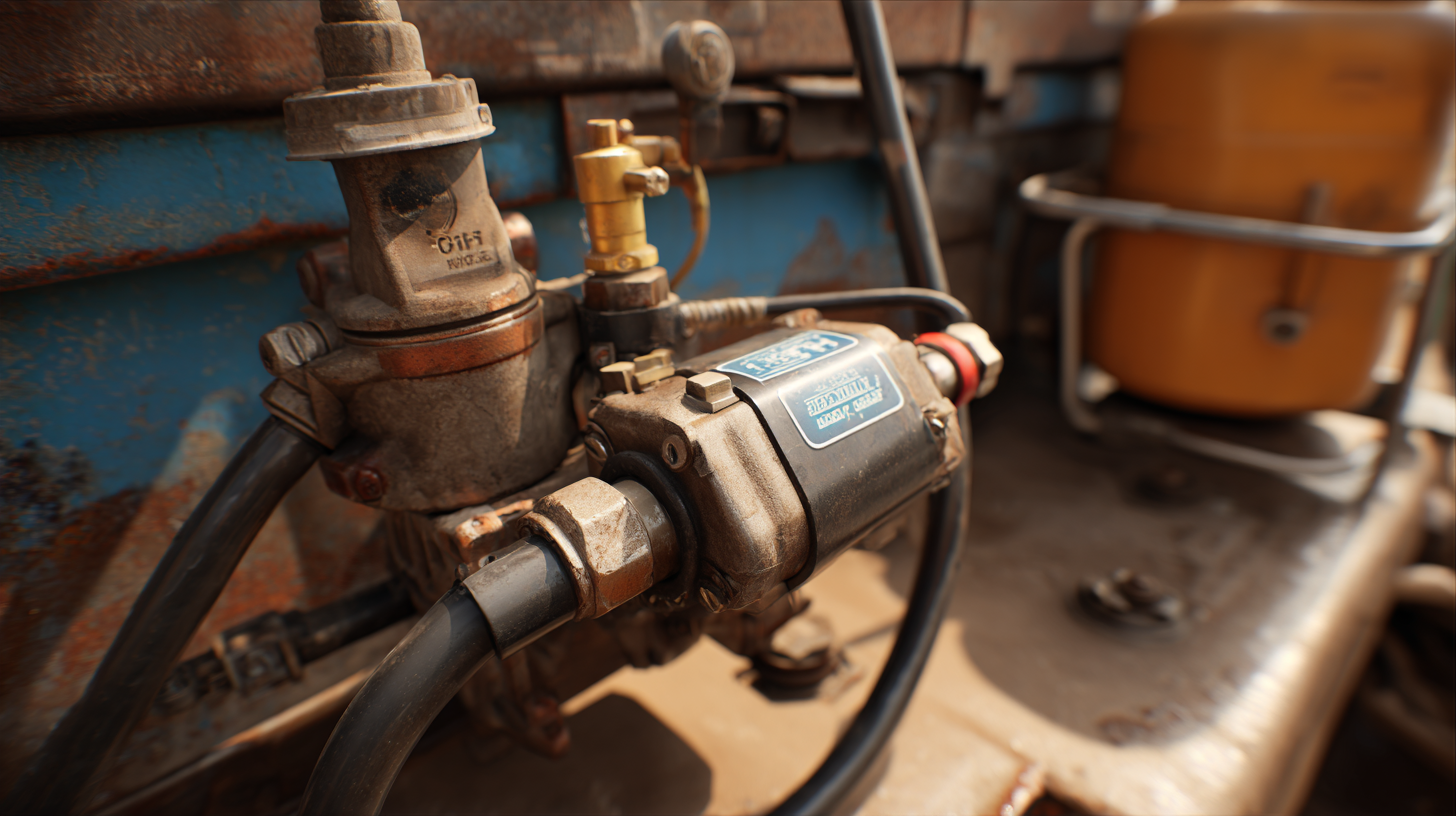

Fuel transfer pumps are essential tools for many industries, but their longevity depends significantly on proper maintenance. To ensure your pump performs reliably, start by regularly checking the oil levels and changing the oil as needed. This will help maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevent wear and tear on vital components.
Another crucial tip is to keep the pump clean and free from debris. Periodic inspection of the pump’s filters and hoses can prevent clogs that reduce performance and can lead to costly repairs. It’s also beneficial to store the pump in a dry, sheltered area when not in use to protect it from environmental factors that could cause corrosion.
Finally, always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for specific maintenance schedules and recommended practices. Keeping a maintenance log can help track any issues and remind you of regular service intervals. By following these tips, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your fuel transfer pump and ensure it functions effectively for years to come.
